We’ve all been in a situation where we accidentally lose an important file. Nothing feels more devastating than feeling powerless when a file is seemingly permanently deleted from your computer.
To help this, Microsoft has released an all-new Windows File Recovery Tool is the latest Windows 10 version 2004.
File recovery is not a foreign concept when it comes to Windows. Users have been creating scripts, commands, and software to recover files that were deleted from the computer. However, an official solution has now been released by Microsoft themselves in the newest version of Windows 10. Here’s the first look and a brief guide on how you can run it.
“For photos, documents, videos, and more, Windows File Recovery supports many file types to help ensure that your data is not permanently lost. Let this app be your first choice for helping to find what you need from your hard drive, SSD (*limited by TRIM), USB drive, or memory cards.” — Windows Store
At the time of writing, the tool hasn’t been updated to a GUI (Graphical user interface) and runs in the Command Prompt. Don’t let this worry you — we’ll include a step-by-step guide on how to use it to recover your long-lost files.
Get Windows File Recovery
How to update Windows 10 to the latest release

Before we begin, you need to have the latest version of Windows 10 installed in order to be able to download Windows File Recovery onto your computer. This can fix bugs, bring you new features, patch up security holes, and much more.
Here’s how you can update Windows 10.
- Click on the Start menu and choose Settings. Alternatively, use the Windows + I keyboard shortcut for quicker access.
- Click on the Update & Security tile.
- Make sure to stay on the default Windows Update tab.
- Click on the Check for updates button.
- If an update is found, click on the Install button and wait for Windows 10 to download and apply the update.
Download the Windows File Recovery tool
After obtaining the latest Windows 10 release, namely Windows 10 version 2004 or newer, you can go ahead and download the File Recovery tool. The guide below details all the steps needed to be able to install the tool on your computer.
- Click on the Start menu and look for the Windows Store. If you can’t locate it, use your computer’s built-in search bar or the Cortana assistant to open the application.
- You might be prompted to log in with an online Microsoft Account. If you don’t have one, head to the Microsoft website and register a new account for free on the signup page.
- After accessing the Windows Store, search for Windows File Recovery or open the store webpage in your browser.
- Click on the Get button to download and install the application. This might take several minutes depending on your internet speed and your system.
-
Once the installation is complete, you can launch the application from your Start menu or Desktop shortcut.
(Source: HTG)
How to use the Windows File Recovery tool
After successfully installing the tool, you’re able to use it to recover your files. If prompted by the UAC (User Account Control), click Yes to allow the Windows File Recovery tool to make changes on your device.
Note: You might be required to enter an administrator password to be able to perform file recovery with this tool. If you don’t have the correct permissions, reach out to someone with a local administrator account to assist you.
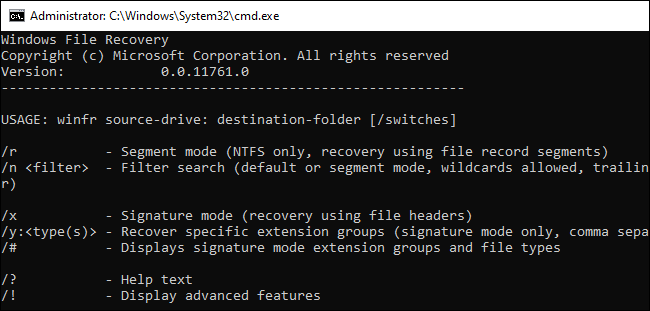
Once the tool has opened, your main command to use will be winfr. You’ll also need to specify a drive for the tool to search for the deleted file, the save destination, and choose between the different modes in the tool.
Here’s the format you can follow:
winfr source-drive: destination-drive: /switches
After running the command, the tool will always automatically create a directory named “Recovery_[timestamp]” in the destination drive. You can navigate to it using File Explorer and check the contents manually.
(Source: HTG)
Configure Windows File Recovery settings
At the time of writing, the tool operates in three different modes in order to optimize different recovery needs and methods.
- Default mode. This mode uses a file table called the Master File Table (MFT) to locate and recover lost files. It is the most basic solution to recovering a file, but it works well when the MFT and File Record Segments (FRS).
- Default mode example: winfr C: E: /n \Users\\Documents\QuarterlyStatement.docx
- Segment mode. This mode does not require the Master File Table (MFT), but does require segments. Summaries of file information that NTFS stores in the MFT such as name, date, size, type, and the cluster/allocation unit index are used to locate and recover lost files.
- Segment mode example: winfr C: E: /r /n *.pdf /n *.docx
- Signature mode. This mode only requires that the data is present on the drive, and searches only for file types. You can use this mode to recover a file on an external storage device, such as a USB drive or external hard disk.
- Signature mode example: winfr C: E: /x /y:JPEG,PNG
To learn more about the three different modes and how you can use commands to customize your recovery, please visit Microsoft’s guide website. The detailed description will guide you in recovering your files as soon as possible.
Final thoughts
We hope this article helped you learn more about the new Windows File Recovery tool released by Microsoft. You’ll never have to worry about an accidentally deleted file in the future.
If you need further assistance regarding the topic, don’t hesitate to reach out to our support team here at Softwarekeep. We’re eager to help you with any technical difficulties you may experience in your day-to-day life.
