With its comprehensive suite of data management functions, Excel provides a powerful tool for efficiently organizing and analyzing data.
By mastering Excel's data management functions, you can gain a competitive edge in your professional life and make informed decisions based on accurate data.
Follow along as we explore the various data management functions and techniques that will empower you to effectively organize and leverage your data.
Table of Contents
- Tips for Data Management in Excel
- Enter Your Data
- Maintain Your Data
- Database Terms: Records and Fields
- Excel's Data Management Tools
- FAQs
- Final Thoughts
Tips for Data Management in Excel
Becoming proficient in Excel goes beyond understanding functions and formulas; it also involves mastering the art of data management. Proper data management is essential for effectively utilizing Excel and maximizing its potential.
Here are some simple tips to help you manage your data efficiently and get the most out of Excel:
- Set up Your Data: Before entering or downloading data, take the time to plan your worksheet structure. Consider these points:
- Plan your headings: Instead of splitting data for categorization, create a column for the category and utilize charts and PivotTables for organizing.
- Avoid hardcoding numbers in formulas: Assign cells to variables and reference them in formulas for easier future editing.
-
Keep your data tight and efficient: Avoid unnecessary formatting with extra headings, subtotals, or empty rows/columns. Utilize charts and graphs for visual representation.
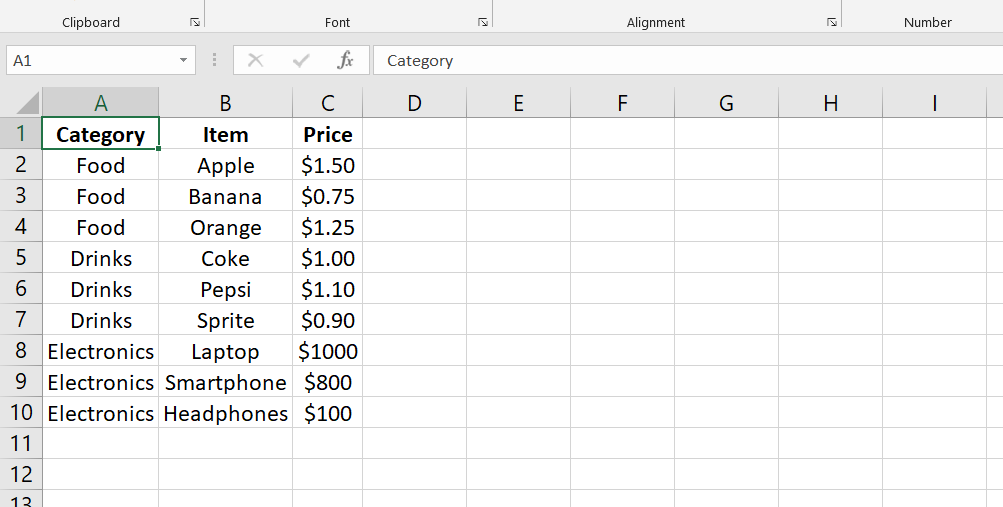
This example has a column labeled "Category" to categorize the items. Instead of splitting the data into multiple columns for categorization, we use a single column and can later utilize charts or PivotTables to organize and analyze the data based on categories.
The prices are not hardcoded directly into the formulas. Instead, they are assigned to cells, such as cell B2 for the Apple price. This allows for easier future editing of prices by simply updating the cell values, and any formulas referencing those cells will automatically recalculate.
The table is kept tight and efficient without unnecessary formatting. There are no extra headings, subtotals, or empty rows/columns. Visual representation can be achieved by creating charts or graphs based on this data.
- Use fixed cell references: Employ fixed cell references in your formulas. This allows for easy copying, pasting, and reusing formulas within the workbook, reducing errors.
- Lock cells with formulas: To protect cells with formulas from accidental changes, lock them:
- Select the entire worksheet using Ctrl+A.
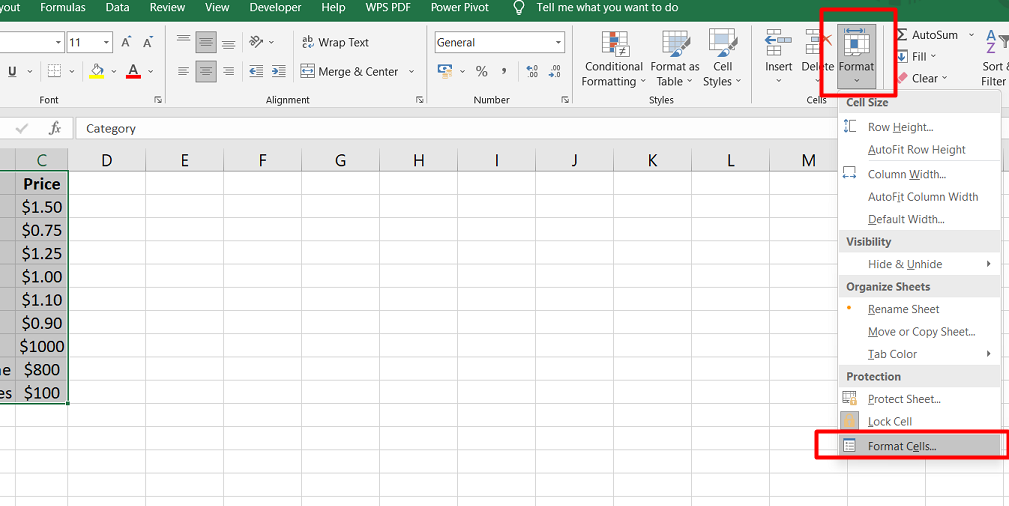
- Click the dialog box launcher in the "Font" group on the Home tab.
-
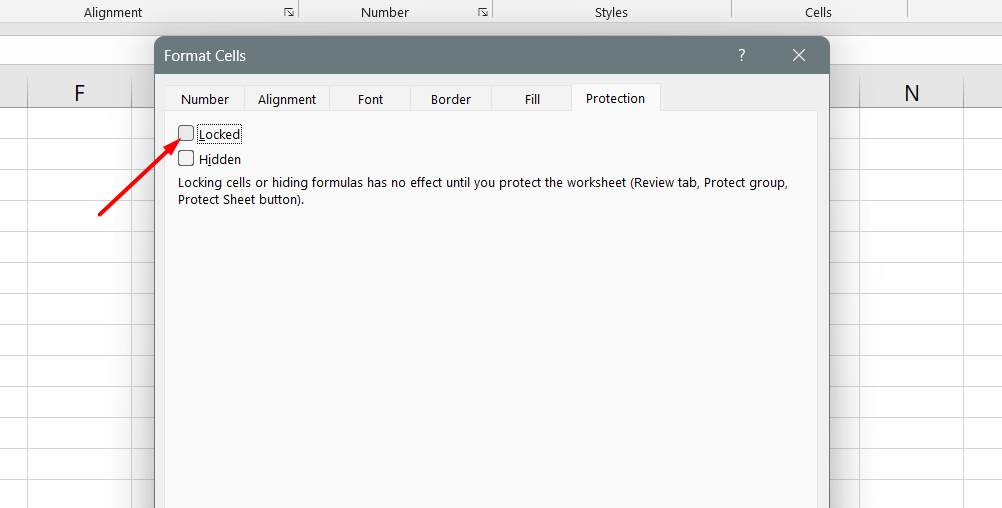
In the "Format Cells" dialog box, go to the "Protection" tab and uncheck "Locked."
-
Select only the cells with formulas, repeat steps 2-3, and recheck "Locked."
-
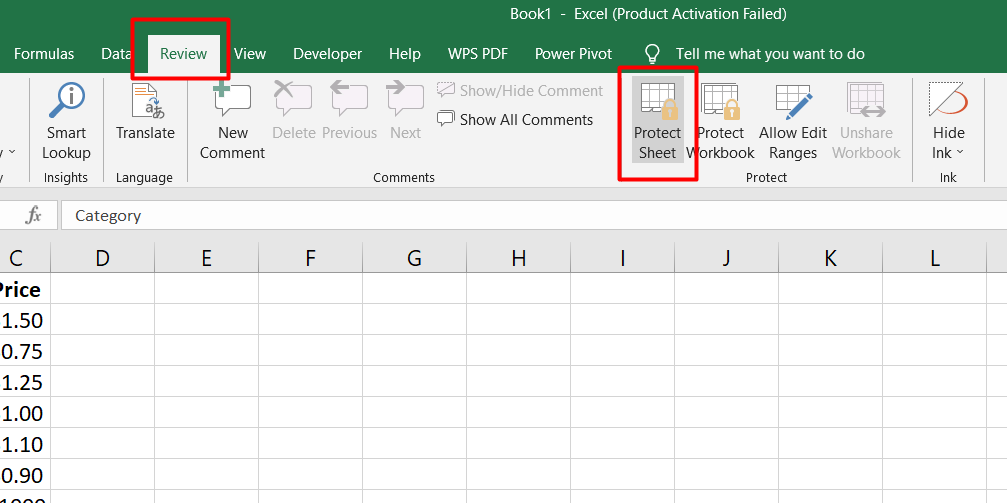
Finally, on the Review tab, click "Protect Sheet."
By following these tips, you can efficiently manage your data in Excel, saving time, ensuring accuracy, and making your data analysis more effective.
Enter Your Data
Once you have set up your tables and workbooks in Excel, it's important to ensure the consistency and accuracy of your data. Here are some tips to help you enter and maintain your data effectively:
-
Use data validation: Utilize Excel's data validation feature to ensure that data formats are correct and common mistakes, such as entering numbers out of range, are caught. Data validation prompts users for correct data and warns them when incorrect entries are made.
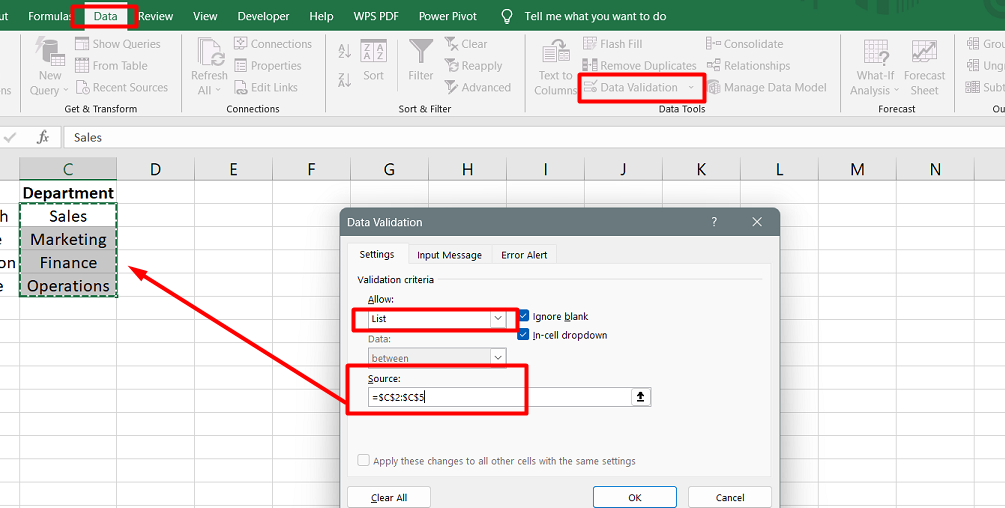
- Consider using forms: If you need to enter data manually, using a form can provide a user-friendly interface that facilitates faster data entry and protects existing data from accidental overwriting.
- Avoid excessive editing of imported data: If you import data into Excel, resist the temptation of reformatting it to match your preferred style. Editing imported data can introduce errors and waste time. Instead, focus on analysis and reporting in separate sheets where you can design the desired look while creating reports.
Maintain Your Data
Over time, as you add and delete records, you may need to perform maintenance tasks on your Excel database. Here are a couple of key points to keep in mind:
-
Backup your database: Before making any changes or performing maintenance tasks, it's crucial to back up your Excel database. Create copies of your original files and store them in a safe place.
If anything goes wrong during maintenance, you can recover your data and start over.
Database Terms: Records and Fields
A database is like a digital collection of information stored in computer files. It helps us keep things organized and easily update sort, correct, and filter data. Let's understand two important terms used in databases:
-
Records: Think of a record as a package that holds all the information about one specific thing in the database. In a database program like Excel, each cell in a worksheet holds one piece of information or value.
So, when we gather all the information about something, like a person or a product, and put it in one row or record, we can easily access and manage that information. -
Fields: In a database record, each piece of information, like a phone number or a street address, is called a field. In Excel, each cell in a worksheet acts as a field because it holds one specific information about something.
For example, a field can be a person's name or age or a product's price or quantity. - Field Names: We use field names to make finding and organizing information in a database easier. Field names are like column headings describing what information each column or field holds. They help us enter data consistently and in the same order for each record.
Understanding records and fields helps us organize and work with data in databases like Excel, making finding and managing the information we need easier.
Excel's Data Management Tools
In addition to its regular features, Excel provides powerful data management tools to handle large amounts of data and maintain its quality. Here are a few of these tools explained simply:
- Using a Form for Records: Excel offers a data form tool that helps you find, edit, enter, or delete records in tables with many columns or fields. The form displays field names and provides text boxes to enter or modify data, ensuring accurate record entry.
-
Remove Duplicate Data Records: In databases, duplicate records can be problematic as the data grows. Excel provides a tool to identify and remove duplicate records, whether they are exact duplicates or have partial similarities.
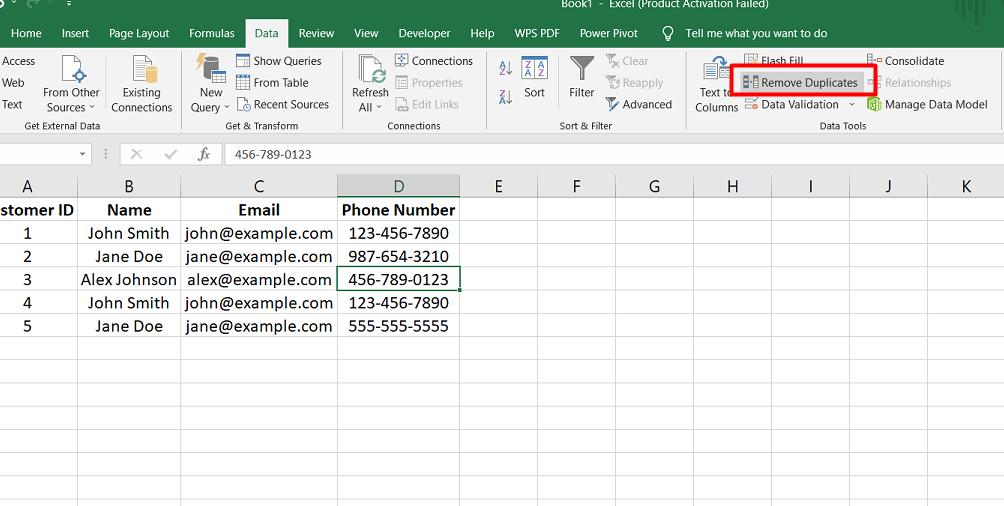
This helps maintain clean and accurate data.
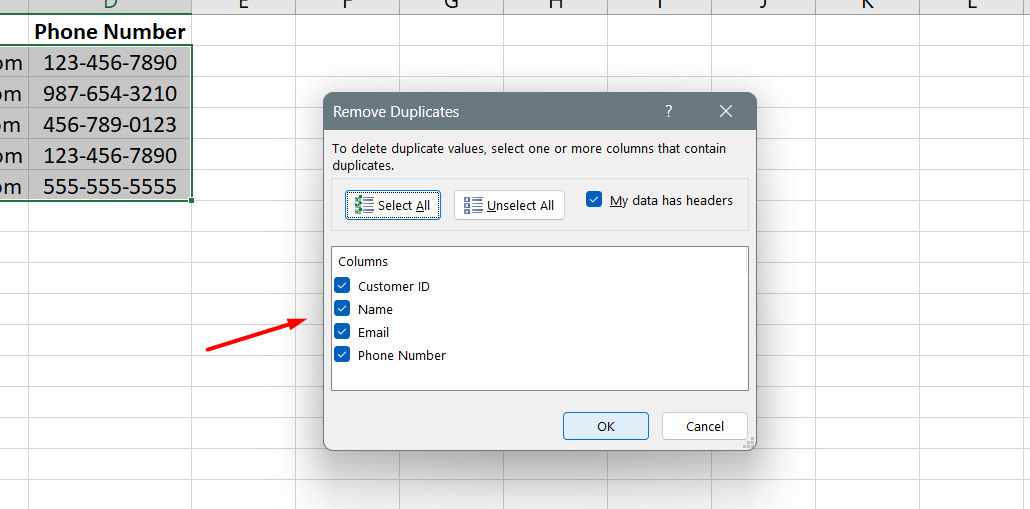
-
Sorting Data in Excel: Sorting means organizing data based on specific properties. Excel's sorting options allow you to sort data alphabetically, numerically, or chronologically.
You can sort by one or more fields, customize the sorting based on dates or times, and even rearrange the order of fields in a table.
These tools in Excel assist in managing and organizing data effectively, making it easier to work with large datasets and maintain data integrity.
FAQs
How do you manage and organize data in Excel?
To manage and organize data in Excel, you can use features such as sorting, filtering, creating tables, and utilizing named ranges to arrange and structure your data effectively.
How do you maintain data in Excel?
To maintain data in Excel, it is important to ensure data accuracy by validating input, using formulas and functions to perform calculations, regularly updating and reviewing data, and implementing data protection measures.
What is the purpose of data management?
Data management aims to collect, organize, store, secure, and utilize data to support decision-making processes, improve operational efficiency, ensure data integrity, and comply with regulatory requirements.
How important is data management?
Data management is crucial as it enables businesses to derive meaningful insights from their data, make informed decisions, enhance productivity, streamline processes, improve customer experiences, and maintain compliance with data protection regulations.
How do we do data management?
Data management involves various practices such as data governance, quality assurance, integration, security, storage, analysis, and lifecycle management to ensure that data is accurate, accessible, secure, and effectively utilized throughout its lifecycle.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Excel provides a range of powerful data management functions that can greatly enhance your ability to organize, analyze, and maintain data. These functions enable you to sort and filter data, create tables and named ranges, validate data inputs, and protect sensitive information.
By utilizing these features effectively, you can ensure data accuracy, improve data organization, and streamline your workflow. Data management is crucial for making informed decisions, improving productivity, and complying with data protection regulations. With Excel's data management functions at your disposal, you can optimize your data management processes and unlock the full potential of your data.
One more thing
If you have a second, please share this article on your socials; someone else may benefit too.
Subscribe to our newsletter and be the first to read our future articles, reviews, and blog post right in your email inbox. We also offer deals, promotions, and updates on our products and share them via email. You won’t miss one.
Related articles
» Sparklines: Creating Meaningful Excel Dashboards with Data Visualization
» How to Use Data Tables in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
» How to Use Conditional Formatting to Make Your Excel Data Stand Out
» Creating a Data Entry Form in Excel: Simplify Your Data Input Process
