The history of Windows dates back to 1981 when Microsoft started work on a program called "Interface Manager." It was announced in November 1983 (after the Apple Lisa, but before the Macintosh) under the name "Windows," but Windows 1.0 was not released until November 1985.
This article aims to take you on a journey through time, highlighting the significant milestones in the evolution of Windows OS.
Join us on this exciting journey as we explore the evolution of Windows OS and discover how it has transformed how we use computers.

Table of Contents
- Introducing Windows 1.0
- Introducing Windows 2.0
- Windows 3: Multitasking, Colorful Interfaces, and Solitaire
- Windows 3.1: TrueType and Minesweeper
- The Arrival of Windows 95
- Windows 98: USB and Multimedia
- Windows ME - Last of 9x
- Windows 2000: Enterprise Edition
- Windows XP: A Classic OS
- Windows Vista Overview
- Windows Vista Editions
- Windows 7: A User-Friendly Upgrade
- Windows 7 Variations
- Windows 8: A Radical Overhaul
- Windows 8 Variations
- Windows 8.1: Start Button Returns
- Windows 10 Unifies Devices
- Variations of Windows 10: Which Edition is Right for You?
- Windows 365
- New Features in Windows 11
- Windows 11 Versions
- Final Thoughts
Introducing Windows 1.0
Windows 1 was the first version of the Windows operating system. It was released in November 1985 and was the first attempt by Microsoft to create a graphical user interface.
This means that instead of typing in commands, users could point and click on icons and buttons on the screen.
Bill Gates, the founder of Microsoft, led the development of Windows 1. It was designed to run on top of a command-line operating system MS-DOS.
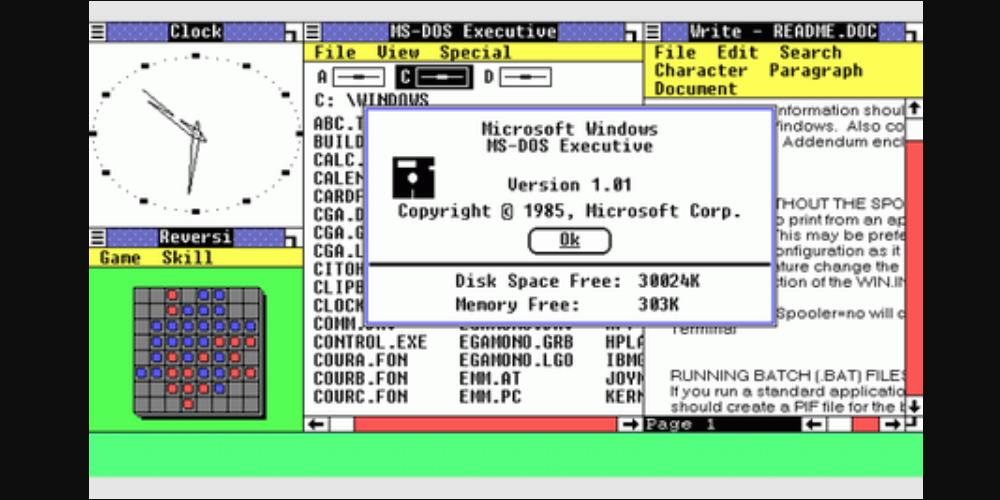
Windows 1 relied heavily on a mouse, which was not a common computer input device. Microsoft included a game called Reversi that required a mouse to help users get used to this new way of interacting with a computer.
Here are some of the key features of Windows 1:
- Graphical user interface (GUI) with drop-down menus, tiled windows, and mouse support
- Device-independent screen and printer graphics
- Cooperative multitasking of Windows applications
Introducing Windows 2.0
Windows 2 was released by Microsoft in December 1987, two years after Windows 1. The biggest improvement in Windows 2 was that windows could overlap each other, making it easier to work with multiple programs simultaneously.
Windows 2 also introduced the ability to minimize or maximize windows, which is still used today.
Another big change in Windows 2 was the introduction of the control panel, which made it easier to find system settings and options. Microsoft Word and Excel were also first released for Windows 2.
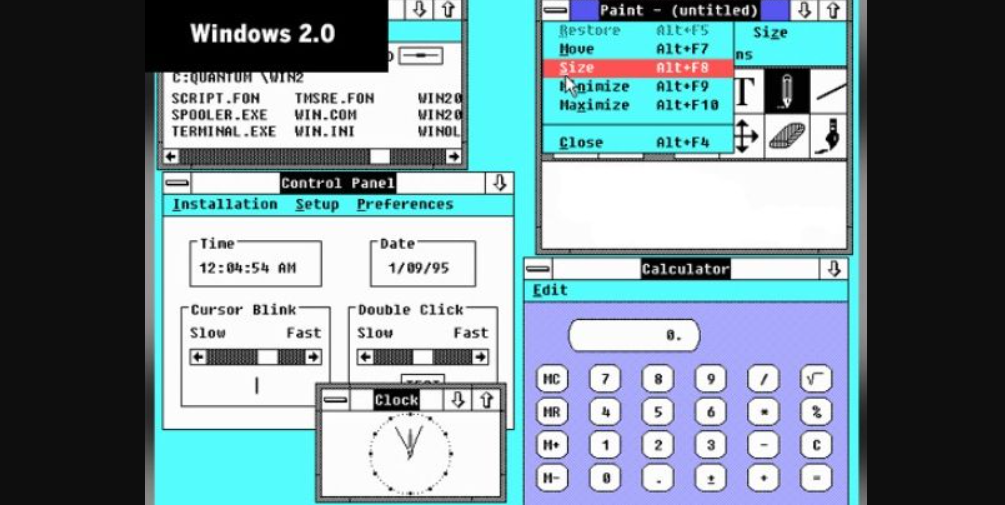
Here are some of the key features of Windows 2:
- Overlapping windows
- Minimizing and maximizing windows
- Control panel for system settings
- Microsoft Word and Excel
Windows 3: Multitasking, Colorful Interfaces, and Solitaire
Windows 3, released in 1990, was the first version of Windows that became popular. It came pre-installed on many PC-compatible computers and allowed users to run multiple programs simultaneously or "multitask."
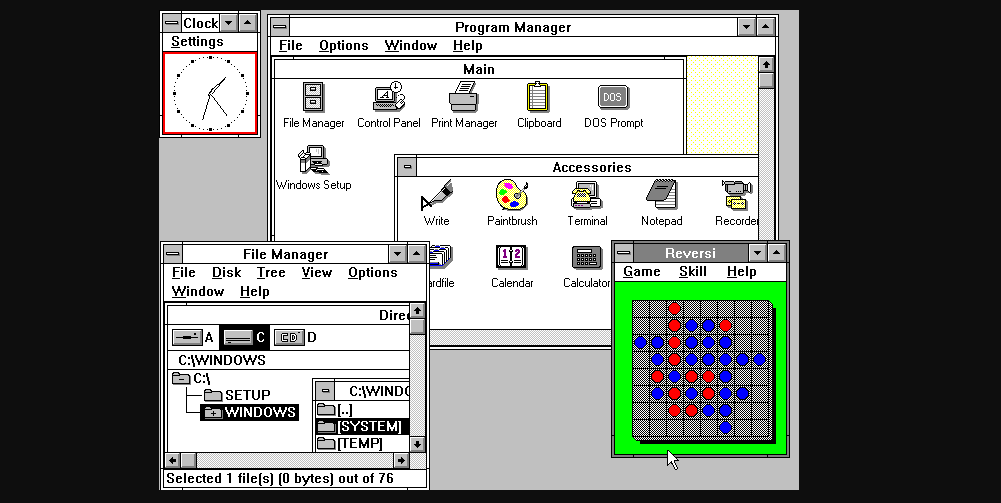
It also had a more modern, colorful look, supporting 256 colors. Among its most prominent features was the card game Solitaire, a big hit with users.
Windows 3 was a big success, selling more than 10 million copies and becoming the best-selling graphical user interface ever.
Windows 3.1: TrueType and Minesweeper
Windows 3.1 was released in 1992 and was an upgrade to Windows 3.0. It was the first Windows version to have TrueType fonts, making it a good publishing platform.
Minesweeper was also introduced in this version. Windows 3.1 required 1MB of RAM and allowed MS-DOS programs to be controlled with a mouse.
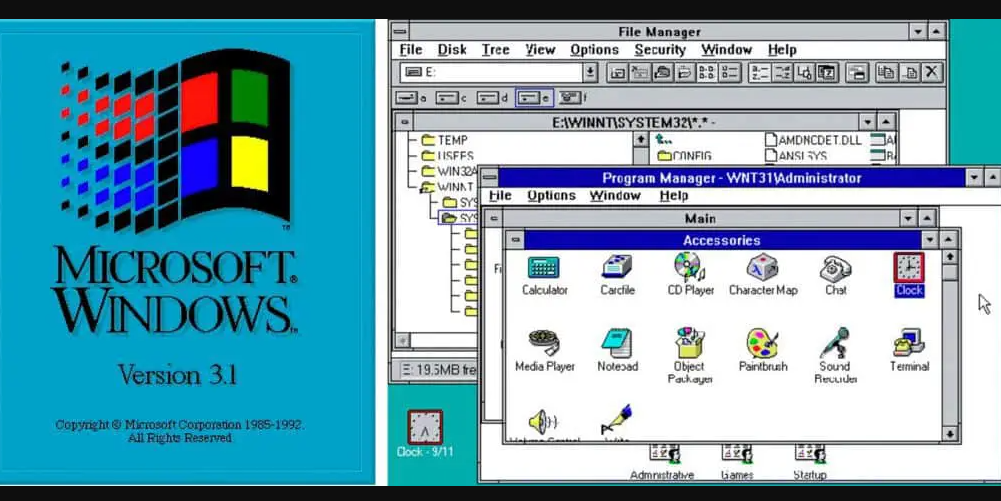
It was also the first Windows version to be distributed on a CD-ROM. The new version sold three million copies in just two months.
The major changes from Windows 3.0 were better multimedia and networking support, TrueType font support, and better error diagnostics.
The Arrival of Windows 95
Windows 95 was released in 1995, and it introduced several new features. The most noticeable change was the Start button and Start menu.

The operating system also introduced the concept of "plug and play," which was supposed to find and install drivers for new peripherals automatically but sometimes didn't work. Windows 95 also focused on multitasking and had a 32-bit environment.
It was designed to work with Windows NT and had greater backward compatibility with older drivers and software. Windows 95 also introduced Internet Explorer but was not installed by default.
Windows 98: USB and Multimedia
Windows 98 was released in June 1998 as an upgrade to Windows 95. It introduced several new features and improvements, such as better support for USB devices and larger hard drives and enhancements to the user interface.
Here are some of the new features and improvements:
-
Improved USB support, which made it easier to connect and use USB devices like mice and printers
- The ability to use larger hard drives and files, thanks to the new file system called FAT32
- Support for multiple monitors so that you can connect more than one screen to your computer
- New programs, such as Internet Explorer 4, Outlook Express, and Windows Media Player
- Improved performance and faster startup times for programs
- Support for DVD-ROM and Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) in the second edition (Windows 98SE)
Windows ME - Last of 9x
Windows ME: The operating system released in 2000 could have been better received by many people because it was known to have many problems. It was the last version of Windows that was based on MS-DOS, and it was intended for home use.
Windows ME introduced new features like automated system recovery tools, IE 5.5, Windows Media Player 7, and Windows Movie Maker. However, it was also known for its bugs and installation issues.
Windows Me was similar to Windows 98SE and included new capabilities for home networking, video editing, and system restoration in case of emergency.
Windows 2000: Enterprise Edition
Windows 2000 was released in February 2000 and was based on the business-focused system Windows NT. It was not an upgrade to Windows 98 or ME.

Windows 2000 was the first to support hibernation, and Microsoft’s automatic updating played an important role. It is built on Windows NT and comes in three varieties: Professional, Server, and Advanced Server.
Windows 2000 offered many improvements, such as stronger internet integration, support for up to 4GB of RAM, and eliminated many reboot scenarios. It also had Windows File Protection, which prevented installed applications from deleting necessary system files.
Windows XP: A Classic OS
Windows XP, released in 2001, combined the best features of Microsoft's enterprise and consumer lines of operating systems. Its interface featured a revamped Start menu, taskbar, Vista wallpaper, and new visual effects.

It also introduced new tools like ClearType, built-in CD burning, and automated updates and recovery tools that worked. While its long lifespan made it popular, its security flaws, especially in Internet Explorer, made it vulnerable to hacking and cyber-attacks.
It had several versions, including Home and Professional, and new editions like Media Center, Tablet PC, and Professional x64.
Windows Vista Overview
In 2007, Microsoft released a new Windows Vista operating system to replace Windows XP. It had a fresh look, with transparent elements and a focus on search and security.
However, it had some problems. Users had to approve every app that wanted to make changes, making people careless with their security.
It was also slow on older computers, despite being labeled "Vista Ready." Windows Vista introduced features like Windows Aero, improved search and multimedia tools, and security enhancements.
However, it was not just an upgrade from XP but a whole new system.
Windows Vista Editions
Windows Vista is an older operating system with different versions and features. Here are the main ones:
- Windows Vista Starter: This version has many limitations for people in developing countries. It only allows using three programs at a time, not letting people share files or printers, and can't play media files.
- Windows Vista Home Basic: This version is for people who want a budget-friendly option for home use. It doesn't have fancy graphics but has some basic features like desktop composition.
- Windows Vista Home Premium: This version is for people who want more features than the basic version. It has better graphics and can burn DVDs. It also supports HDTV and Xbox 360.
- Windows Vista Business: This version is for people who use their computers for work. It has all the features of the Home Basic version plus the ability to join a Windows server domain.
- Windows Vista Enterprise: This version is for big businesses with extra features like BitLocker and UNIX application support.
- Windows Vista Ultimate: This version has all the features of the Home Premium and Business editions. It also has access to "Ultimate Extras" and can support up to two physical CPUs.
Windows Vista's mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012, and extended support ended on April 11, 2017. It was replaced by Windows 7, and as of February 2022, only 0.18% of PCs run Windows Vista.
Windows 7: A User-Friendly Upgrade
Windows 7 was released in 2009 as the successor to Windows Vista. It aimed to fix users' problems and complaints with Vista and was considered a huge improvement.

Windows 7 was faster, more stable, and easier to use, and many people upgraded to it from Windows XP, skipping Vista entirely. Some new features in Windows 7 included handwriting recognition and the ability to snap windows to the sides of the screen for easier resizing.
Microsoft faced antitrust investigations in Europe over the pre-installation of Internet Explorer, which led to the introduction of a browser ballot screen.
Windows 7 Variations
Windows 7 is a popular operating system with five versions: Starter, Home Premium, Professional, Enterprise, and Ultimate. However, there are also special versions of Windows 7 called the "N editions."
These N editions of Windows 7 give you the freedom to choose your own media player and other software to manage and play digital media files, like CDs and DVDs.
Here are some things you might want to know about Windows 7 N editions:
- Windows 7 N editions are special versions of Windows 7 that let you choose your own media player and other software to manage and play digital media files.
- The regular versions of Windows 7 come with a built-in media player called Windows Media Player, but the N editions don't have it pre-installed.
- If you want to use Windows Media Player or other software to manage your digital media files, you must download and install it yourself.
- The N editions of Windows 7 are available in the same five editions as the regular versions: Starter, Home Premium, Professional, Enterprise, and Ultimate.
- Choosing an N edition of Windows 7 might be good if you have your preferred media player or other software to manage and play your digital media files.
On January 14, 2020, Microsoft ended security updates and technical support for Windows 7 after 10 years. This means that Microsoft is no longer supporting Windows 7.
Windows 8: A Radical Overhaul
Windows 8 was launched in 2012 with a completely new interface with the Start button and Start menu replaced with a more touch-friendly Start screen. The new interface had program icons and live tiles displaying information like "widgets."
A desktop interface similar to Windows 7 was still available. Windows 8 was faster than its predecessors and introduced support for USB 3.0 devices.

The Windows Store was introduced, which offered universal Windows apps, but third-party programs could only access the traditional desktop interface. However, the new touch-oriented interface wasn't welcomed by traditional desktop users, who preferred using a mouse and keyboard.
Windows RT, a version for ARM-based processors, was also introduced.
Windows 8 Variations
Windows 8 has four editions: Windows 8.1 Pro, Windows 8.1, Windows 8.1 Enterprise, and Windows RT 8.1. The first two are available for regular people to buy. The third is for big organizations, and the last is for special devices with ARM processors.
All three editions of Windows 8 mentioned above come in two versions: 32-bit and 64-bit. If you want to upgrade the standard version of Windows 8.1 to Windows 8.1 Pro, you can buy the Windows 8.1 Pro Pack on Amazon.
Windows RT 8.1 only runs the software that comes with it or that you can download from the Windows Store. You can't install regular Windows software on it.
Windows 8 and 8.1 are no longer sold, but you can try to find them on Amazon or eBay if you really need them.
Here's a summary of the different Windows 8 editions:
- Windows 8.1 Pro: for regular people who want extra features
- Windows 8.1: for regular people who don't need the extra features
- Windows 8.1 Enterprise: for big organizations
- Windows RT 8.1: for special devices with ARM processors
Windows 8.1: Start Button Returns
Windows 8.1 was a free update released in October 2013 that aimed to address some of the criticisms of its predecessor, Windows 8.

It included reintroducing the Start button, which was missing from Windows 8, and the option to boot directly into the desktop view, better suited for users with a mouse and keyboard.
Microsoft also began to shift towards yearly software updates with this release.
Windows 10 Unifies Devices
Windows 10 is the latest version of Microsoft’s operating system, announced in 2014 as a “technical preview” available for testing. It returns the Start menu and balances traditional desktop computers and touch-based devices like tablets.

Windows 10 is designed to unify all platforms across multiple devices, allowing universal apps to be downloaded from the Windows Store and run on all Windows devices. It also includes switching between keyboard, mouse, and tablet modes for devices like the Surface Pro 3.
Windows 10 was set to be released in 2015 after Microsoft’s developer conference.
Variations of Windows 10: Which Edition is Right for You?
Windows 10 comes in several variations, each with its own set of features that cater to different needs. Here are the different versions of Windows 10 and what they offer:
Windows 10 Home: This standard version of Windows 10 comes pre-installed on most PCs sold to consumers. It's designed for ease of use and has features such as built-in security with Windows Defender, the ability to sign in using your face or fingerprint with Windows Hello, and bundled software such as Microsoft Photos.
Windows 10 S: This special mode of Windows 10 restricts users to only downloading software from the Microsoft Store. It's designed to keep your computer more secure and running smoothly.
Windows 10 Pro: This version of Windows 10 offers all the features of Home edition, plus tools used by businesses such as enhanced encryption options and the ability to create and run virtual machines.
Windows 10 Enterprise: This version of Windows 10 is only available to businesses that purchase a volume license. It includes most of the features of Pro, but with additional tools that allow IT administrators to manage aspects of employees’ PCs remotely.
Windows 10 Education: This version of Windows 10 is designed for schools and universities to provide staff and students with Windows 10. It has similar features to Windows Pro, but some elements of the OS, such as the Microsoft Store, can be turned off by default.
Windows IoT: This special version of Windows is designed to run on low-powered smart devices such as touchscreen displays. It's available to download from Microsoft's developer site and can be installed on a Raspberry Pi.
However, Microsoft is ending support for Windows 10 on October 14, 2025. Find out what this means and how to prepare before it's too late.
Watch: Raspberry Pi Alternatives - Cheaper, Faster, More Software
Windows 365
Windows 365 is a cloud-based computing service from Microsoft that allows users to stream a full Windows desktop experience on any device with an internet connection. It provides a virtualized environment with customizable options for storage, processing power, and memory to meet the needs of individuals or organizations.
Users can access their personalized desktop from anywhere, with their settings and files saved securely in the cloud. This eliminates the need for physical hardware upgrades and maintenance and makes it easier for companies to manage and scale their computing needs. Windows 365 is available in two editions:
- Business
- Enterprise
New Features in Windows 11
Windows 11 is the latest version of Microsoft's operating system, which was released in late 2021. It has some new features, including changes to the look and feel of the interface, a new widget system for quick access to information, and the ability to snap windows into different layouts.
The default apps have been updated, and a redesigned settings app makes it easier to change system settings. Users can also now have multiple desktops, which can be used to organize their work more efficiently.
Teams is also now integrated into the system, making it easier to collaborate with colleagues. Additionally, there are new accessibility features, including system-wide live captions and more natural voices for the Narrator.
Windows 11 Versions
Here's an overview of the three editions of Windows 11:
- Windows 11 Home: This is the basic version of Windows 11 designed for home users. It comes with all the essential features of Windows, such as the new Start menu, Taskbar, virtual desktops, and the ability to run universal Windows apps.
- Windows 11 Home is ideal for users who need basic functionality and do not require advanced management or security features.
- Windows 11 Pro: This version of Windows 11 is designed for small businesses and advanced users. It includes all the features of Windows 11 Home and adds extra capabilities such as Windows Update for Business, Hyper-V virtualization, BitLocker encryption, and Remote Desktop.
- Windows 11 Pro is ideal for businesses that need advanced management and security features.
- Windows 11 Enterprise: This version of Windows 11 is designed for large organizations and enterprises. It includes all the features of Windows 11 Pro and adds even more capabilities such as Windows Defender Application Guard, Windows Sandbox, and Credential Guard.
- Windows 11 Enterprise is ideal for organizations requiring the highest security and management features.
Final Thoughts
The Windows operating system has come a long way since its first release in 1985.
With each new version, Microsoft has introduced new features and improvements, responding to user feedback and technological advancements.
From the early days of Windows 1 to the latest version of Windows 10, the operating system has significantly shaped the way we use computers today.
One more thing
If you have a second, please share this article on your socials; someone else may benefit too.
Subscribe to our newsletter and be the first to read our future articles, reviews, and blog post right in your email inbox. We also offer deals, promotions, and updates on our products and share them via email. You won’t miss one.
