Are you wondering how to restart Windows update related services? Here's a guide to restarting Windows Update related services using three methods.

Windows Update is an essential component of Windows operating system, and is more important in Windows 10 and 11.
It allows downloading and installing the latest updates with bug fixes, security patches, and drivers. It also helps download new feature updates and preview builds.
But sometimes your device may not download or install updates because of a specific error message, Windows Update not connecting to the Microsoft servers, and other problems.
If you're experiencing issues with Windows Update, restarting the Windows Update related services can often resolve the problem.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to restart Windows Update related services using various methods.
What are Windows Update Related Services?
Windows Update related services are a set of services that are responsible for managing and delivering Windows updates to your computer. These services are integral to the Windows Update process and ensure that your computer remains up to date with the latest build, security, and feature updates.
There are four main services considered as Windows Update related services:
- Windows Update Service (wuauserv): Enables the detection, download, and installation of updates for Windows and other programs.
- Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS): Transfers files in the background using idle network bandwidth.
- Cryptographic Services (CryptSvc): Provides essential cryptographic services in Windows, including those used for Windows Update. Cryptographic Services is a Microsoft Windows feature that encrypts and decrypts data on storage devices when they are accessed. It can be used for user authentication to archive encryption or decryption.
- MSI Installer (msiserver): This service installs, modifies, and removes Windows software packages, including Windows updates.
These services work together to ensure that updates are downloaded and installed properly on your computer.
If any of these services stop working or encounter errors, it can prevent updates from being installed, causing issues with your computer's performance and security.
Restarting these services is a common troubleshooting step when encountering issues with Windows Update.
Why Restart Windows Update Related Services?
There are several reasons/situations why you might want to restart Windows Update related services:
- Windows Updates are failing: If your computer is unable to download and install Windows updates, restarting the related services can often fix the problem. This is because the services may have stopped working properly and need to be restarted.
- Windows Update is taking too long: If Windows Update is taking a long time to download or install updates, restarting the related services may speed up the process. This is because the services may be stuck or not functioning properly, causing the update process to slow down.
- Windows Update is stuck: If Windows Update is stuck on a particular update, restarting the related services may help to unblock the update process. This is because the services may be preventing the update from installing properly.
- Fixing Windows Update errors: If you encounter any error messages while trying to download or install updates, restarting the related services may help to fix the errors. This is because the services may be responsible for the errors.
In general, restarting Windows Update related services is a simple troubleshooting step that can help to resolve a wide range of issues related to Windows Update. Always try this step if you're experiencing any issues with Windows Update before moving on to any complex solutions.
How to Restart Windows Update Related Services in Windows 10/11
Here are 3 methods to restart Windows updated related services:
- Use the command prompt
- Use the services console
- Use Windows update troubleshooter
Let’s discuss them in detail below.
Method 1: Using the Command Prompt
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
-
Type "cmd" and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
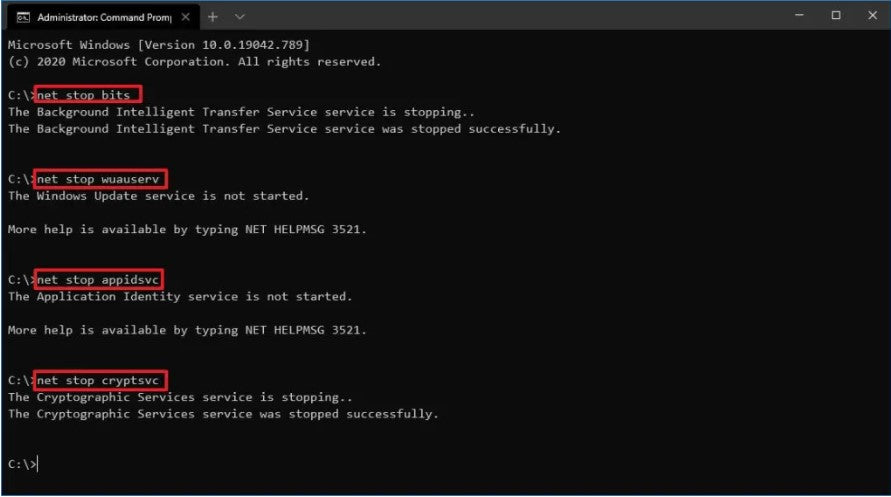
- Type the following commands, one at a time, and press Enter after each one:
- net stop wuauserv
- net stop cryptSvc
- net stop bits
-
net stop msiserver
- Type the following commands, one at a time, and press Enter after each one:
- net start wuauserv
- net start cryptSvc
- net start bits
- net start msiserver
- Close the Command Prompt and check if the issue is resolved.
Method 2: Using the Services Console
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
-
Type "services.msc" and press Enter to open the Services console.
- Scroll down to find the following services:
- Windows Update
- Cryptographic Services
- Background Intelligent Transfer Service
- MSI Installer
- Right-click each of these services and select "Stop" to stop them.
- Right-click each of these services again and select "Start" to start them.
- Close the Services console and check if the issue is resolved.
Method 3: Using the Windows Update Troubleshooter
- Press the Windows key + I to open the Settings app.
- Click on "Update & Security."
- Click on "Troubleshoot" in the left-hand menu.
- Scroll down and click on "Windows Update" under "Get up and running."
- Click on "Run the troubleshooter" and follow the prompts.
- Once the troubleshooter has finished, restart your computer and check if the issue is resolved.
Final Thoughts
Restarting Windows Update related services can often resolve issues with Windows Update.
By using the Command Prompt, Services console, or Windows Update troubleshooter, you can easily restart these services and get Windows Update back up and running.
We’re glad you've read this article upto here :) Thank you for reading.
One more thing
If you have a second, please share this article on your socials; someone else may benefit too.
Subscribe to our newsletter and be the first to read our future articles, reviews, and blog post right in your email inbox. We also offer deals, promotions, and updates on our products and share them via email. You won’t miss one.